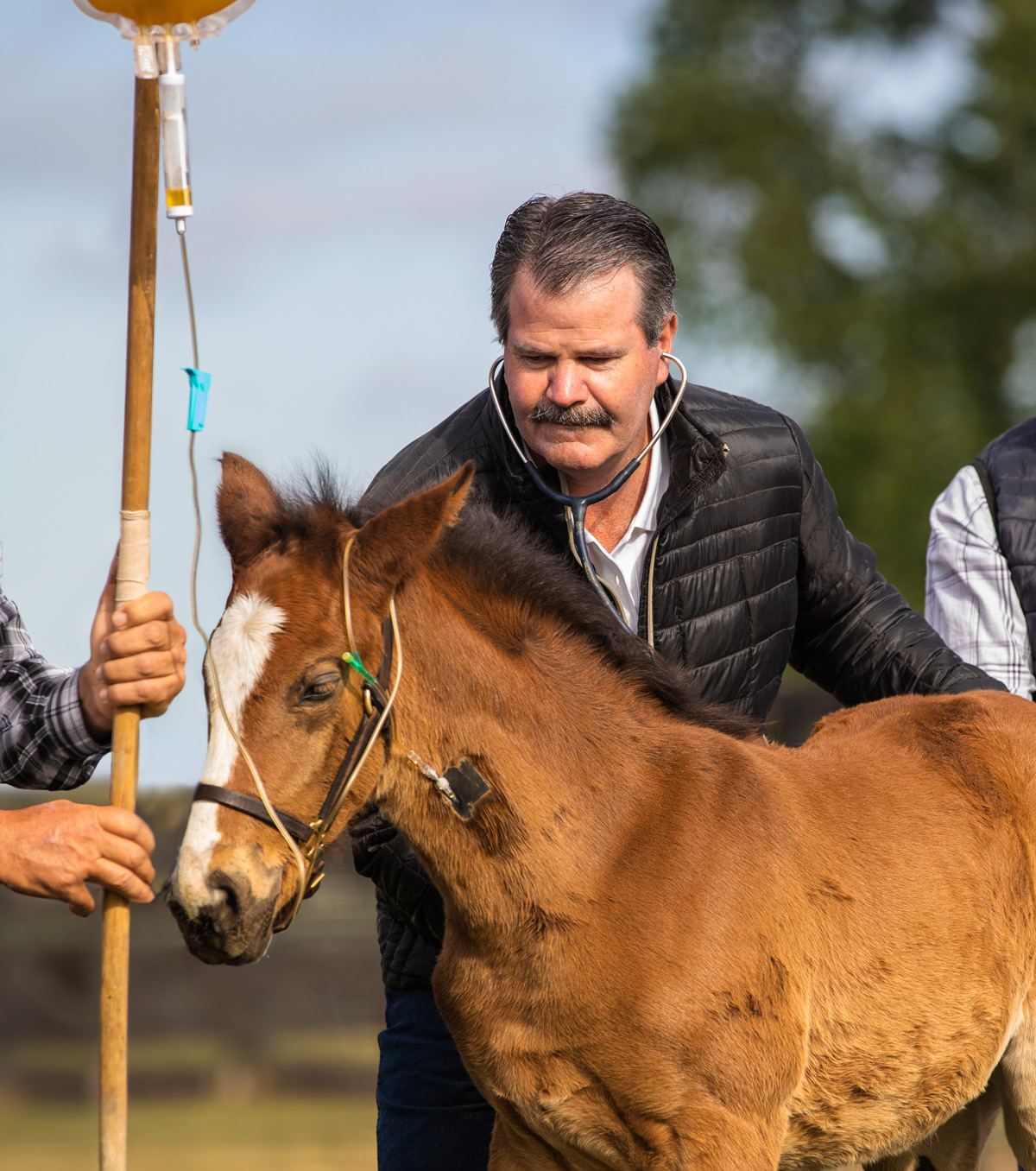
What is Plasma Therapy?
Plasma therapy is the process of administering plasma or plasma-based products to increase the levels of antibodies in the blood. When used to complement conventional veterinary treatments, plasma therapy shortens the course of treatments, reduces hospitalization periods and lessens the quantity of drugs required to treat a wide variety of medical conditions. Plasma therapy also has a host of preventative applications.
The blood of all mammals has four key constituents:
- Red cells - cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to body tissues
- White cells - cells responsible for producing antibodies that counteract infectious microorganisms
- Platelets- cells that aid the clotting process
- Plasma- the liquid component of blood containing proteins, antibodies or gamma-globulins, clotting factors and a variety of other immunity-boosting agents
The liquid portion of uncoagulated mammalian blood that is free of cells is known as plasma.
Plasvacc products contain hyperimmunized plasma, a form of plasma that has greatly increased levels of antibodies. Hyperimmune plasma can only be obtained from donors subject to a formal hyperimmunization regimen. This involves the strategic administration of a variety of commercial and proprietary vaccines enabling Plasvacc products to target specific active infections. In response to hyperimmunization, donors accumulate levels of antibodies in their bloodstream 2-3 times higher than those of normal animals.
Plasma is extracted from blood samples using a complex centrifugal process. In order to obtain plasma sufficiently rich in gamma-globulins (antibodies), Plasvacc plasma is derived solely from the blood of hyperimmunized donors.